
Overview of Earned Value Management
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a comprehensive project management technique used to assess project performance and progress. EVM integrates data regarding actual costs incurred, planned costs, and the monetary value of completed work to evaluate the project’s current status in terms of budget and schedule. Additionally, EVM enables the estimation of future project performance and outcomes.
Calculating Earned Value Management
The foundation of EVM is the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). Each component within the WBS must be individually analyzed, with progress tracked for each work package. Completion rates are assigned as follows:
- 100% for fully completed tasks
- 0% for tasks not yet started or partially completed
For partially completed tasks, various methods such as the 50-50 rule, 0-100 percent rule, and critical input use rule can be applied. However, for simplicity, this discussion will assume a binary approach (0% or 100%) for completion rates.
Key Metrics in Earned Value Management
To effectively apply EVM, the following concepts are crucial:
Earned Value (EV): The budgeted amount for the work accomplished to date.
Actual Cost (AC): The actual expenditure for the work performed.
Planned Value (PV): The budgeted cost for the work scheduled to be completed by a specific date.
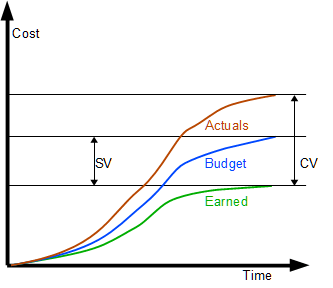
These metrics should be continuously calculated and plotted to monitor deviations from planned performance and address any discrepancies.
Detailed Analysis of EVM Indices
Cost Variance (CV)
Formula: CV = EV – AC
Interpretation: A negative CV indicates that the project is over budget, meaning actual costs have exceeded planned expenditures.
Schedule Variance (SV)
Formula: SV = EV – PV
Interpretation: A negative SV indicates that the project is behind schedule.
Cost Performance Indicator (CPI)
Formula: CPI = EV / AC
Interpretation: A CPI less than 1 indicates that costs have exceeded the budgeted amount.
Schedule Performance Indicator (SPI)
Formula: SPI = EV / PV
Interpretation: An SPI less than 1 indicates that the project is progressing slower than planned.
Forecasting Future Project Performance
EVM also allows for future performance estimations through the following calculations:
Estimate to Complete (ETC)
Formula: ETC = (BAC – AC) / CPI
Purpose: Determines the remaining budget needed, assuming current performance trends continue.
Estimate at Completion (EAC)
Formula: EAC = AC + ETC
Purpose: Provides an estimate of the total project cost at completion.
To Complete Performance Indicator (TCPI)
Formula: TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (BAC – AC)
Purpose: Indicates the necessary cost performance for the remaining work to meet a specific management goal.
While other indices such as TPI and TV offer additional insights, the accuracy of EVM largely depends on the precise reflection of work completion percentages. Consistent monitoring and adjustment based on EVM metrics enable more effective project management, ensuring projects stay within budget and on schedule.
